Over 50 million Americans are suffering from autoimmune diseases each and every day. To put that into perspective, that’s 20% of the population. For many, the complications associated with the disease can be debilitating. In the past, suppressive therapy has been used to treat these diseases using steroids to try and control the immune response in the body. Today, we are helping patients find new solutions using innovative stem cell therapy.
There is a long list of disorders in which our body’s own immune system becomes the enemy and attacks the body. This group of disorders is commonly referred to as autoimmune diseases or connective tissue disorders. Stem cells have already shown effectiveness in treating autoimmune diseases and have promise for even greater results in the future. This article will discuss the following issues of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases:
1. What autoimmune disorders can consider stem cell therapy?
2. Why consider stem cell deployment for autoimmune disease?
3. How are adult stem cells deployed for autoimmune disease?
4. What results can I expect after stem cells therapy for autoimmune diseases?
5. What is the future for adult stem cells for autoimmune diseases?
What Autoimmune Diseases Can Consider Stem Cells?
Stem cells from fat are highly anti-inflammatory when deployed in most patients. This makes them of great interest in autoimmune disease. A complete list of disorders for which stem cells have been used would be extensive. Some of the disorders that have benefited are:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease
- Discoid Lupus
- Fibromyalgia
- Crohn’s Disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Lyme Disease
- Scleroderma (Progressive Systemic Sclerosis)
- Alopecia Areata
- Pulmonary Fibrosis (see more under lung disease)
Other autoimmune diseases may also be candidates on an individual basis.
A: Autoimmune neuropathy is a painful peripheral nerve condition that occurs because of autoimmune disease. Peripheral neuropathy often occurs in the hands, feet, and lower legs, and patients with the condition experience pain, sensations of tingling or numbness, and muscle weakness. Patients with neuropathy often experience extreme sensitivity to touch. These symptoms can impact a patient’s ability to walk or do everyday activities. Patients with severe cases of autoimmune neuropathy experience feelings of burning, excessive sweating, paralysis. Some autoimmune neuropathy patients have organ, gland, or body system dysfunction or failure. Traditional treatment for peripheral neuropathy includes treating the underlying disease, plasma exchanges, steroids, and pain-relieving medications to help manage the painful symptoms, but do not heal the damaged nerve tissue. Some patients require physical therapy. See our web page Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, or CIDP, is a nerve disorder that causes inflammation of the peripheral nerves. It also destroys the myelin sheath, the protective covering of the nerves, and ultimately leads to damage and loss of nerve tissue. CIDP impacts how the brain and the body communicate and leads to weakness, loss of motor function, and paralysis. The severity of symptoms varies from patient to patient. Standard treatments for CIDP include steroids and immunosuppressant drugs, intravenous globulin, and plasma exchanges.
Stem Cell Therapy for CIDP and Autoimmune Neuropathy
For patients with autoimmune neuropathy and CIDP, Innovations Stem Cell Center deploys SVF stem cells through IV along with injections. Damaged tissue attracts stem cells through growth factor chemical messages, and deployed stem cells find the damaged or diseased tissue and begin repairs. Stem Cell therapy for autoimmune neuropathy is performed at both our Dallas and Fort Worth practice locations.
Patients begin seeing results in the first few weeks of treatment. Some patients may require additional deployment.
A: Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles are what allows the body to move, breath, make facial expressions, talk, or swallow. Signs of myasthenia gravis include muscle weakness that occurs after activity, drooping eyelid, or drooping mouth. Other effects of the disease include difficulty breathing or speaking, impaired vision, and difficulty walking. Treatments for myasthenia gravis manage symptoms, but do not cure the disease. Treatments include medications, blood transfusions, steroids, and in severe cases, surgery to remove the thymus gland.
Stem Cell Therapy for Myasthenia Gravis
For patients with myasthenia gravis, Innovations Stem Cell Center deploys SVF stem cells through IV along with injections. Damaged tissue attracts stem cells through growth factor chemical messages, and deployed stem cells to find the damaged or diseased tissue and begin repairs. Stem cell procedures for Myasthenia Gravis are performed at both our Dallas and Fort Worth practice locations.
Patients begin seeing results in the first few weeks of treatment. Some patients may require additional deployment.
A: Autoimmune hepatitis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the liver. The disease causes inflammation and can lead to cirrhosis of the liver or liver failure. Symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis include fatigue, joint pain, yellowing of the skin, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Some autoimmune hepatitis patients are swelling of the liver, weight loss, and mental confusion or disorientation. Patients with autoimmune hepatitis are treated with steroids to reduce inflammation of the liver, but long-term use of steroids can cause complications like high blood pressure, weight gain, glaucoma, and lower the immune system’s ability to fight off infection.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Hepatitis
For patients with autoimmune hepatitis, Innovations Stem Cell Center deploys SVF stem cells through IV along with injections. Damaged tissue attracts stem cells through growth factor chemical messages, and deployed stem cells to find the damaged or diseased tissue and begin repairs. Innovations Medical performs stem cell procedures for Autoimmune Hepatitis at both our Dallas and Fort Worth practice locations.
Patients begin seeing results in the first few weeks of treatment. Some patients may require additional deployment.
A: Relapsing polychondritis is a rare autoimmune disorder of the cartilage that causes recurring inflammation throughout the cartilage in the body. The disorder can affect anywhere there is cartilage in the body, including the joints, nose, and ears. The trachea can also be affected. Other tissues, like the eyes, heart, and blood vessels, have a structure like that of cartilage can also be affected by the disorder. Symptoms of the condition include a sudden onset of pain, redness, swelling, and stiffness. Some patients with relapsing polychondritis experience deformity in their tissues, as well as an impairment to hearing and balance, along with fever, nausea, and vomiting. Relapsing polychondritis in the trachea can cause difficulty breathing. If the condition affects the eyes, vision loss can result. Patients with polychondritis inflammation of the heart can experience damage to the aorta, leaving them at risk for aneurysm.
Stem Cell Therapy for Polychondritis
For patients with relapsing polychondritis, Innovations Stem Cell Center deploys SVF stem cells through IV along with injections. These stem cell procedures are performed at both our Dallas and Fort Worth practice locations. Damaged tissue attracts stem cells through growth factor chemical messages, and deployed stem cells find the damaged or diseased tissue and begin repairs.
Patients begin seeing results in the first few weeks of treatment. Some patients may require additional deployment.
Why Consider Stem Cells for Autoimmune Disease?
Conventional treatment for autoimmune diseases has improved greatly in recent years. Unfortunately, conventional treatment often falls short in resolving all symptoms of autoimmune disease. In addition, conventional treatment can have significant side effects including increased risk of infection and long term cancer risk. Stem cells have the ability to regulate the immune system. To read further on stem cells read our blog What are Stem Cells? They can help turn off the overactive parts of our immune system that tend to attack our tissues. Stem cells do this while leaving the rest of our immune system intact. They can also help promote healing in areas of immune system damage. This combined ability of stem cells to regulate the immune system and promote healing makes them of extreme interest to patients with autoimmune diseases.
How Are Adult Stem Cells Deployed?
When we give stem cells back to patients we refer to it as deployment. Almost every patient with autoimmune disease receives an intravenous (IV) deployment. In addition, other areas are such as specific joints are often injected. For example, a rheumatoid arthritis patient might receive injections in both knees in addition to IV. A Chron’s disease patient could receive injections around open fistulas. There are other possibilities depending on disease and area of involvement. All harvests of fat and deployments of stem cells occur on the same day. See our blog Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
What Results Can I Expect?
Results have been encouraging for stem cell therapy for autoimmune disease, although some diseases have only small numbers of patients in the database. Some examples are:
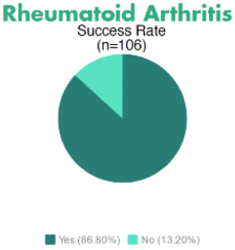
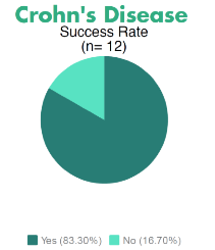
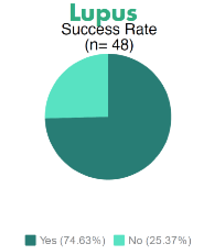
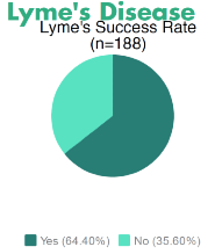
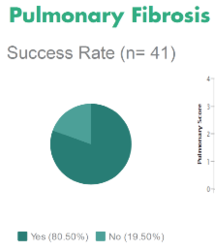
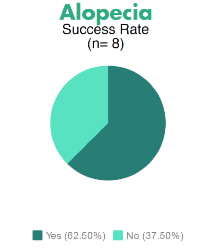
Many other diseases have received stem cell therapy, but data remains unavailable at this time.
Cost of Stem Cells Treatments
The cost of the initial treatment ranges from $5,000 to $10,000. The range in cost is dependent on the complexity of delivering the cells back to you. For example, spine conditions require multiple physicians to deliver the cells back to your body and this requires an increase in cost as multiple doctors are involved in the procedure. For many people the initial treatment is all that is needed; however, for some conditions, subsequent treatments may be required and these are done at a reduced fee.
What Is the Future of Adult Stem Cells?
Many experts believe that stem cells will play a central role in treating autoimmune diseases in the future. Stem cells’ ability to regulate the immune system makes them especially valuable for autoimmune diseases. The near future will bring better ways to deploy the cells and a better understanding of how many cells are needed and how often we should deploy. The future should also see lowered costs and the ability to store and grow cells for future use.
