How Well Do Stem Cells Work for Peripheral Neuropathy?
The most important questions for potential patients seeking stem cell treatment for neuropathy is: “Do they work?”. This has been the subject of many published studies. Although there is much work left to be done, we can answer some questions:
Answer: Yes in many cases. Most studies show evaluating pain show improvement. This includes diabetic and non-diabetic cases. While many studies show the effectiveness of stem cells for neuropathic pain in animals, human studies much fewer. Expect many advancements in the next few years.
Answer: Yes in many cases. The situation is similar to that with pain. Studies do show improvement, but the best way to collect and deliver the stem cells is still being determined.
Answer: Yes in many cases. Patients with neuropathy often have balance problems. Stem cells appear to do help much of the time.
Answer: Yes in many cases. Nerve regeneration is seen in many animal studies and a few human studies. Again, the best ways to collect and deliver the stem cells are still being determined.
In the Cell Surgical Network, over 50% of all patients respond, remember most of these patients have tried and failed many other treatments.
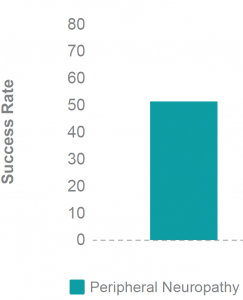
We use stem cells from your own fat to help with peripheral neuropathy.
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a group of disorders that share abnormal function of “peripheral nerves”. Peripheral nerves are the part of our nervous system that is NOT part of the brain or spinal cord (central nervous system). Neuropathy describes a disorder where there are problems with the peripheral nerves but not the central nervous system.
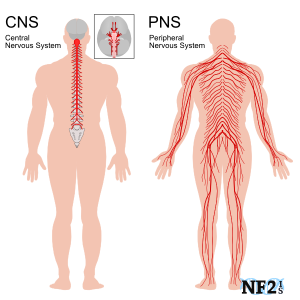
Although there are many forms of peripheral neuropathy, they tend to cause the same symptoms. Everyone is a little different, but most patients have a burning/tingling pain, numbness, and occasionally weakness.
What is the Traditional Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy?
There are several disorders that can cause peripheral neuropathy. Some causes such as a B12 deficiency can be treated and resolved with traditional medical techniques. Many other forms are poorly understood and referred to as idiopathic. Idiopathic forms are hard to treat using traditional medical techniques. Medications are used to help the pain when present, but very little can be done for numbness or weakness. Many patients can have pain relief with traditional medications, but the response is limited and there are some side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer: Most commonly, peripheral neuropathy begins as a loss of sensation or burning in the feet or hands. This tends to be fairly equal in both hands and feet. Weakness may be associated in some cases. The exact pattern by which the disease develops is determined by the underlying cause.
The most common causes of peripheral neuropathy are:
- Diabetes mellitus. This is the most common cause. Studies show that about 42% of diabetics develop peripheral neuropathy. Burning, Tingling, and Pain
- Other systemic. This includes vitamin deficiencies, hypothyroidism, HIV infection, and others.
- Autoimmune. This category includes Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Toxic. The most common toxin is alcohol. Chemotherapy and lead exposure along with others are also in this category.
- Hereditary.
- Environmental. This is most commonly from injuries such as repeated vibrations or severe hypothermia.
- Idiopathic. This means the cause is unknown. Up to 25% of cases fit into this category.
Most of these disorders affect the sensory nerves causing loss of sensation and frequent pain or discomfort. Many of them, especially the autoimmune peripheral neuropathies, also affect motor function. Symptoms can vary from very mild (often diagnosed by accident while looking for other disorders) to severe and debilitating.
For more information see: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/peripheral-neuropathy
Answer: When possible, like with diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, treatment begins with treating the underlying cause of the peripheral neuropathy. Removing toxins such as alcohol or environmental factors like repeated vibration can also be instrumental in these disorders. Patients with autoimmune neuropathy are sometimes treated with aggressive therapies such as:
- Intravenous immune globulin.
- Plasma exchange.
- High dose steroids (glucocorticoids).
Other treatments are directed toward helping the symptoms and avoiding complications. Several medications are used to help with the pain and discomfort:
- Gabapentin and other anti-epilepsy drugs like carbamazepine and topiramate.
- Tricyclic antidepressant drugs like amitriptyline desipramine.
- Pain medications like tramadol or ibuprofen.
Physical therapy is also very important to train in walking and balance assistance. Proper training and maintenance of routine foot inspection are essential to prevent or intervene early with foot and leg ulcers. If you are a person doing well using these options, this might not be the right time to consider adult stem cell treatment. However, if you are not doing well with the current treatment, you may wish to consider adult stem cell treatment. For more information on the treatment of peripheral neuropathy please see:
https://www.webmd.com/brain/understanding-peripheral-neuropathy-treatment#1
Answer: Stem cells are special cells in our bodies that have two important characteristics:
- Stem cells have the ability to replicate. In other words, they can make new copies of themselves. Because of this ability, an infinite number of copies can be made from the same cell.
- Stem cells also have the ability to become other types of cells. A good example of this is that research labs have used fat-derived stem cells to make cartilage muscle, skin, and bone cells. This ability means that in theory the transformed can make an infinite number of the new cell type. See our blogs What are Stem Cells? and Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Stem cells can come from a number of sources including embryos, umbilical cord blood, and adult cells. Adult stem cells come from adult individuals, not embryos or umbilical cord blood. Stem cells obtained from mature adult tissues are referred to as adult stem cells. Adult stem cells are believed to have the potential to become any type of cell.
The two most commonly used sources of adult stem cells are fat and bone marrow.
Adult stem cells from fat are called adipose-derived adult stem cells. For most purposes, stem cells from fat are easier to obtain and more abundant than from other tissues.
Answer: Harvesting adult stem cells from fat is very safe. The procedure has little discomfort and a fairly easy recovery. First, an area such as the stomach or leg is picked to remove the fat. We then take you to the procedure room and sterilize the area. A local anesthetic is then injected into the area. Fat is suctioned using a special syringe and cannula. Typically we suction about 50 ml (about 1 1.2 oz.) of fat.
Swelling and bruising are common following the procedure at the harvest site. Swelling and bruising typically resolve within 2-3 weeks after the procedure. Most patients receive a prescription for pain medications for use as needed. We give a dose of antibiotics before the procedure but no antibiotics are needed afterward.
Nest we take the harvested cells and use a centrifuge and incubator to do some simple processing. The processing isolates the adult stem cells from the other fat cells. The final product is called Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF). SVF obtained from fat can contain up to about 25 million adult stem cells from 50 ml of fat. SVF also contains a large amount of growth factors. Growth factors are chemical “text messages” our cells use to communicate with each other. After we have obtained the SVF, the next step is to deploy the SVF for your peripheral neuropathy.
Answer: Once the process of removing adult stem cells/SVF from fat is complete, we then deploy them for peripheral neuropathy. All types of peripheral neuropathy are treated with IV deployment. For the autoimmune peripheral neuropathies, we often give a special IV medication known as mannitol which is believed to enhance adult stem cell/SVF penetration into the brain. We know that the damaged areas are releasing growth factors. These growth factors attract the adult stem cells/SVF to the area of the injury or disease activity.
In treating the non-autoimmune peripheral neuropathies we also deploy the adult stem cells/SVF into the soft tissue around the area of nerve involvement. We use a small needle and inject the adult stem cells/SVF about 1 centimeter deep every few centimeters in the areas of the involved nerves.
Answer: Currently, the treatment group is not large enough to give a conclusive answer to this question. Federal Court has confirmed that giving you stem cells taken from your fat is a surgical procedure. Since the FDA does not regulate surgeries, this type of procedure cannot be FDA approved or disapproved. Fortunately, we have enough early experience to talk about trends in therapy. The number of patients treated increases weekly, so the total depends on when you are reading this article (initial writing October 2013). The majority of patients with toxic, autoimmune, and environmental peripheral neuropathy respond well. Responses usually begin in a few weeks to months. Some patients do have a second deployment, typically between 3 and 12 months depending upon their response. Patients with diabetic or idiopathic peripheral neuropathy only respond about one-third (1/3) of the time. Performing the second deployment may help this percentage somewhat, but does not appear to dramatically increase response rates.
Answer: Many people believe that stem cells hold great potential for treating and reversing the effects of peripheral neuropathy. The type of stem cells best to use (embryonic, bone marrow, or fat derived) and how to best utilize them is heavily researched and debated. Adult stem cells have a good chance of becoming the treatment of choice because of their safety, availability, and lack of controversy. It is likely that in the future, we will see further preparation done to the adult stem cells/SVF in order to prepare them to more readily become neurons. Over the next few years, we have some real hope in seeing therapy develop that could restore large amounts of function to patients with peripheral neuropathy.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
The cost of the initial treatment ranges from $5,000 to $10,000. The range in cost is dependent on the complexity of delivering the cells back to you. For example, spine conditions require multiple physicians to deliver the cells back to your body and this requires an increase in cost as multiple doctors are involved in the procedure. For many people the initial treatment is all that is needed; however, for some conditions, subsequent treatments may be required and these are done at a reduced fee.
Contact Innovations Medical to Learn About Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
If you’re looking to treat peripheral neuropathy, Innovations Medical is here for you. Our skilled professionals help you decide which treatment is best for you, keeping you informed and confident in the next steps. We’ve been helping our patients look and feel their best since 2005, and even our most advanced procedures are often minimally invasive.
To find out if stem cell therapy is right for you, and to learn how Innovations Medical can improve your life, call us at (214) 643-8665 or request a consultation.
